RPA development cycle
Overview
When a new bot request is approved or the improvement of an existing bot has been created, you can manage the development cycle in Bizagi. The development cycle of a bot is based on a normal development procedure: first, the bot is developed by a user entitled as a RPA developer stakeholder; second, a user entitled as a RPA tester stakeholder performs tests to validate errors and report bugs if required; finally, when all the issues have been fixed, the same tester publishes the bot to production.
The following image represents the development cycle of a bot:
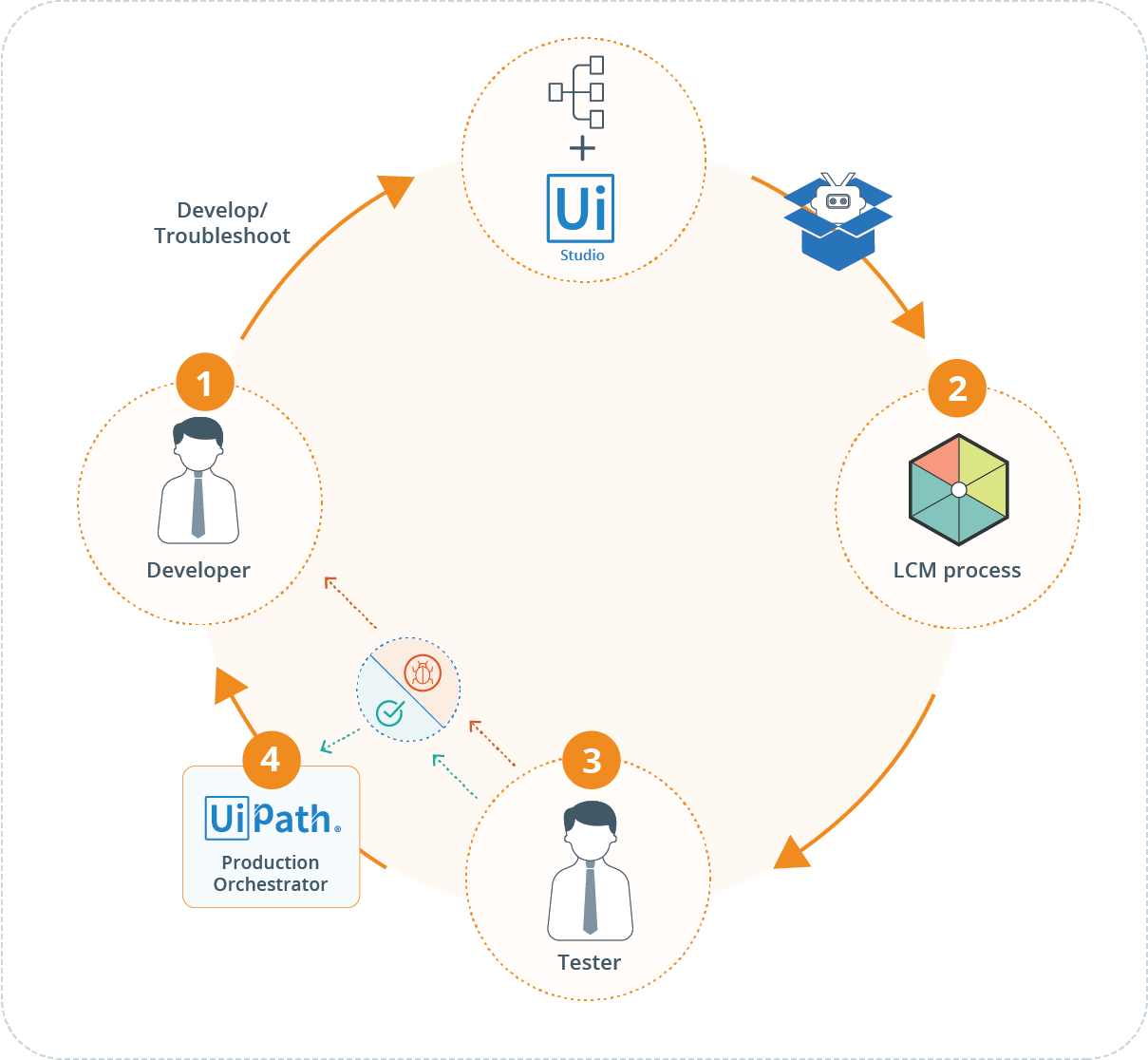
The development cycle in the RPA life cycle management process includes the following steps:
- Bot development: Create or improve the bot according to the requirements document generated in the Request new RPA process or Improving existing bots.
- Upload the bot package to Bizagi: Once the package associated with the bot is created in UiPath Studio, locate its .nupkg file in your project's path. Then, upload it to the Orchestrator in the development environment.
- Send the bot to test: When the bot has been associated with a process in an environment, the bot changes its status in Bizagi and is assigned to a user entitled as a RPA tester stakeholder. This user performs tests and checks whether the bot is ready to be in the Production environment.
- Report bugs: If the tester finds issues related to the functional or non-functional requirements, they report them to the developer so they can fix them and send the bot back to test.
- Send the bot to Production: When the tester approves the bot, they send it to the production environment. When the tester sends the bot to production, the bot goes through an approval process.